Pick to: with acoustic emission techniques monitoring of fracture process of intermetallic compound, and connecting with the scanning electron microscopy (sem) and metallographic analysis studies the sofar
Radiation characteristics and the relationship of the rupture, points out the shortage of grain boundary strength is lead to material at the root of low stress rupture, and described the process of breaking, from a different perspective to the study of such material provides a reference value to the analysis of the basis.
Key words: acoustic emission; Intermetallic compound. Breaking process
1 lead it
Intermetallic compound is nearly 30 a to a hotspot of research on high temperature structural materials, combines with metallic bonding and superlattice structure with long range order, make it may be better with metal plasticity and high temperature strength of the ceramic, thus become the aerospace engine potential new materials. But due to its poor plasticity and fracture toughness at room temperature, it is difficult to processing molding, yet can be widely used in engineering.
ChanZhiWei [1], such as direct observation by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) in situ tensile crack initiation of Ni3Al single crystal and along the zigzag path extension process, the author USES acoustic emission technology from another Angle to study the deformation behavior of the intermetallic compound and fracture process. Acoustic emission technology in ceramic materials have been applied in the study of [2, 3], but little of intermetallic compound research reports. Author at room temperature compression test was carried out on the Ni3Al and Ni3Si, using acoustic emission technology to monitor the crack dynamic propagation process, to analysis the fracture behavior of intermetallic compounds in the process of deformation. By observing the changes in the form of crack, and concluded that the fracture mechanism, thus help to improve its plasticity.
2 sample preparation and test method
2.1 sample preparation
Sample material for the as_cast Ni3Al and Ni3Si intermetallic compound, made of different diameter of sample, the purpose is to obtain different dependent variable, amount of compression compression test and the corresponding load are shown in table 1.
2.2 test method
Will probe coupling on the tester sample clamp, record collection and acoustic emission signals during the process of test, the probe center frequency of 100 KHZ, pre_amplifier gain 40 db, total gain of 85 db. SF - 02 a acoustic emission instrument of analog signal output into transient waveform storage, and through the synchronous oscillograph real time observation, use function recorder record peak level real_time output. Mistras - 2001 acoustic emission system synchronized acoustic emission monitoring. After test with S - 520 scanning electron microscope (SEM) and Neophot32 optical microscope for microstructure analysis, to explore organizational change and the correlation of acoustic emission, so as to describe fracture in acoustic emission process.
3 test results and analysis
3.1 acoustic emission signal load - displacement curve
1 # ~ 4 # sample records of Ni3Al curve with a consistent characteristics - editor). Under low load can be a large number of acoustic emission signals, can be thought of in the elastic_plastic stage produce acoustic emission phenomenon intensive activities, along with the load increase, the material into the plastic deformation stage, at this time of the acoustic emission signal in steady state, the naked eye, can be observed that the propagation of the crack but not split until the maximum load sample testing machine.
Ni3Si 1 # ~ 3 # sample is consistent characteristics (figure slightly - editor), and in the process of compression and Ni3Al similar characteristics. For the study of causes of acoustic emission regions and low stress, the author of Ni3Al # 5 sample and Ni3Si 4 # sample just across the acoustic emission signal in the activity zone respectively, namely after the elastic stage, then stop loading, and then respectively sampling for metallographic analysis.
3.2 metallographic analysis
3.2.1 SEM morphology characteristics of crack
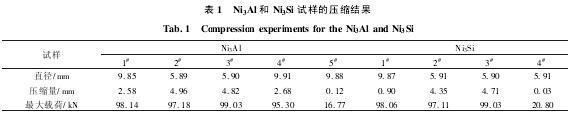
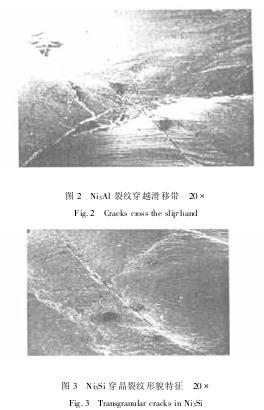
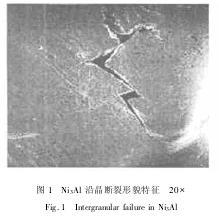
From figure 1 shows, Ni3Al sample can be obviously glide step, after compression crack extended along the grain boundary. Load in large strain (> 95 kn), observed some crack through the slip band (figure 2). And Ni3Si along with the increase of the dependent variable are more transgranular crack (figure 3).
3.2.2 crack forms
After the compression test of different deformation of Ni3Al and Ni3Si sample preparing metallographic specimen respectively, and uncompressed sample as the original tissue. Analysis shows that Ni3Al primitive coarse grains and dendrites developed. Ni3Si original organization of large amount of two phase region, grain boundary is not obvious, and the two phase region surrounded by a single silicon phase precipitation.
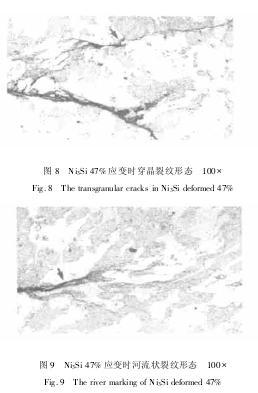
Figure 4 shows that Ni3Al in elastic_plastic deformation stages along the grain boundary cracking has occurred, it has to do with acoustic emission signal from the result of the observation on the load - displacement curve is consistent, namely in the elastic_plastic stage there is a large number of acoustic emission signals. Along with the rising of the dependent variable, cracks along the grain (figure 5). Further increasing the dependent variable, then in the intergranular crack propagation at the same time produce transgranular cracks (figure 6). Also, figure 7 shows Ni3Si along the grain boundary in elastic_plastic stage of the second phase boundary surface wider, and micro cracks on the edge of the precipitated phase. Along with the rising of the dependent variable, crack along the interface extension of the second phase (figure 8), and further increase the crack tip should be variable in the second phase distortion, rivers shaped, crack along the deformation after second phase interface or through the second phase of extension (figure 9), particularly in the area of slip band stagger. That the results obtained with the acoustic emission signal is consistent, namely in the elastic-plastic stage there is crack initiation.
Ni3Si compared with Ni3Al, load to load the initial acoustic emission signal is less, this is due to the crack initiation of Ni3Al too early, but Ni3S at first is that the second phase interface get wide crack, no big crack. Long and Ni3Si elastic stage, crack initiation extension mainly concentrated in the elastic stage, and the yield point nearby. Ni3Al except near the elastic stage and the yield point, in the whole of acoustic emission signals during the compression process, suggesting that Ni3Al easier than Ni3Si to brittle fracture. Ni3Al and Ni3Si acoustic emission behavior of intermetallic compound compression process shows that this materials in elastic_plastic deformation phase, the a large number of acoustic emission signal, the metallographic analysis found that the phase boundary width of crack or along the crystal formation in the micro inclusions in micro crack.
Increases as the dependent variable, the acoustic emission signal in a steady, metallographic analysis shows that Ni3Al and Ni3Si stable crack extended along grain boundary, at the same time this materials intracrystalline presents good plasticity, have obvious slip, should continue to increase variables are transgranular cracks occurred.

4 conclusion
(1) the acoustic emission technique can effectively display material breakage process of crack initiation and propagation characteristics.
(2) Ni3Al, Ni3Si grain boundary strength weak is a major cause of lead to deformation processing craze, strengthen the intensity of grain boundary is the key to improve the performance of deformation processing. And Ni3Si strength is insufficient, the second phase in the compression process presents the obvious deformation, strength is weak, and the second phase and matrix interface should be variable in big crack in the substrate along the two phase interface extension, forming a large number of transgranular crack.
References (abbreviated)





